Precision Lighting in Data Centers: How Photocells and Occupancy Sensors Reduce Waste and Downtime
- Why Sensor-Based Lighting Matters in Data Centers
- What Photocells Do and Why They’re Smart for Data Centers
- How Occupancy Sensors Work Inside Data Centers
- Real-World Benefits: Not Just “Energy Efficient” on Paper
- Best Practices for Installing Sensors
- Integration With CAE Lighting Systems
- Challenges We’ve Run Into—and Solved
- Are Photocells and Occupancy Sensors Worth It?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Key Takeaways
| Area | Insight |
|---|---|
| Photocell Functionality | Light-responsive; ideal for daylight harvesting and outdoor controls |
| Occupancy Sensor Types | PIR, Ultrasonic, and Dual-Technology sensors enhance lighting automation |
| Integration Benefits | Up to 30% energy savings; better cooling, reduced load on HVAC/lighting |
| Installation Advice | Calibrate based on room geometry; avoid signal-blocking objects |
| Ideal Products | Squarebeam Elite and Quattro Triproof Batten work well with sensors in server environments |
| Key Use Cases | Cold aisles, utility corridors, exterior perimeters, electrical rooms |
| Real-World ROI | Some deployments recover costs in 12–18 months with minimal maintenance |
Why Sensor-Based Lighting Matters in Data Centers
Data centers eat electricity like snack food. Lighting, while not the main draw like HVAC or server load, still quietly racks up costs and heat. But we’ve seen firsthand in installations across Malaysia that just changing the way lights behave saves more than most people expect.
- Photocells handle the natural light bit. Think skylights and glass corridor walls.
- Occupancy sensors? They flip lights off when nobody’s around. Smart and silent.
What Photocells Do and Why They’re Smart for Data Centers
Photocells react to visible light levels. Here’s what that means:
- If it’s bright outside, they keep artificial lights off.
- When clouds roll in or daylight fades? Lights flip on—automatically.
Main use cases in data centers:
- Skylit corridors
- Entryways with windows
- Outdoor perimeter lighting
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Photovoltaic | Generates voltage under light; common in daylight harvesting |
| Photoconductive | Resistance changes with light; often more precise |
| Photoemissive | Less common; uses emitted electrons when exposed to light |

How Occupancy Sensors Work Inside Data Centers
There are no naps in server rooms—but there are gaps in foot traffic. That’s where occupancy sensors shine.
Three core types:
- PIR (Passive Infrared): Detects body heat movement.
- Ultrasonic: Uses sound waves to “see” motion (works through partitions).
- Dual-tech: Combines both for accuracy in complex spaces.
Best applied in:
- Electrical rooms
- Underfloor wiring paths
- Patch panel corridors
Real-World Benefits: Not Just “Energy Efficient” on Paper
Let’s strip the buzzwords and talk numbers:
- Energy Use Reduction: Up to 30% in areas with low traffic
- HVAC Synergy: Less heat from lights = less work for cooling
- Operational Savings: Lowered runtime = extended luminaire lifespan
- Compliance Boost: Helps meet ISO and local energy codes
We installed a SeamLine Batten system in a mid-size data hall—occupancy-controlled. ROI was 13 months, and it cut energy use by a third.

Best Practices for Installing Sensors
Getting this wrong means flickering lights or dead zones. Here’s what we’ve learned over 40+ projects:
- Don’t block sensors with racks, piping, or suspended cable trays
- Position PIR sensors at doorways; ultrasonic ones in center ceilings
- Set time delays: 5 mins for storage, 20 mins for workstations
- Calibrate each unit manually—auto mode usually overshoots
| Area | Sensor Type | Mounting Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Hallways | PIR | Aim perpendicular to walking paths |
| Server Corridors | Dual-Technology | Place in central beam, 2.4–3m height |
| Electrical Rooms | Ultrasonic | Cover entire volume, even around gear |
Integration With CAE Lighting Systems
CAE’s fixtures are built with sensor integration in mind. Some products, like the Budget High Bay Light, support external sensor add-ons and pre-wiring options.
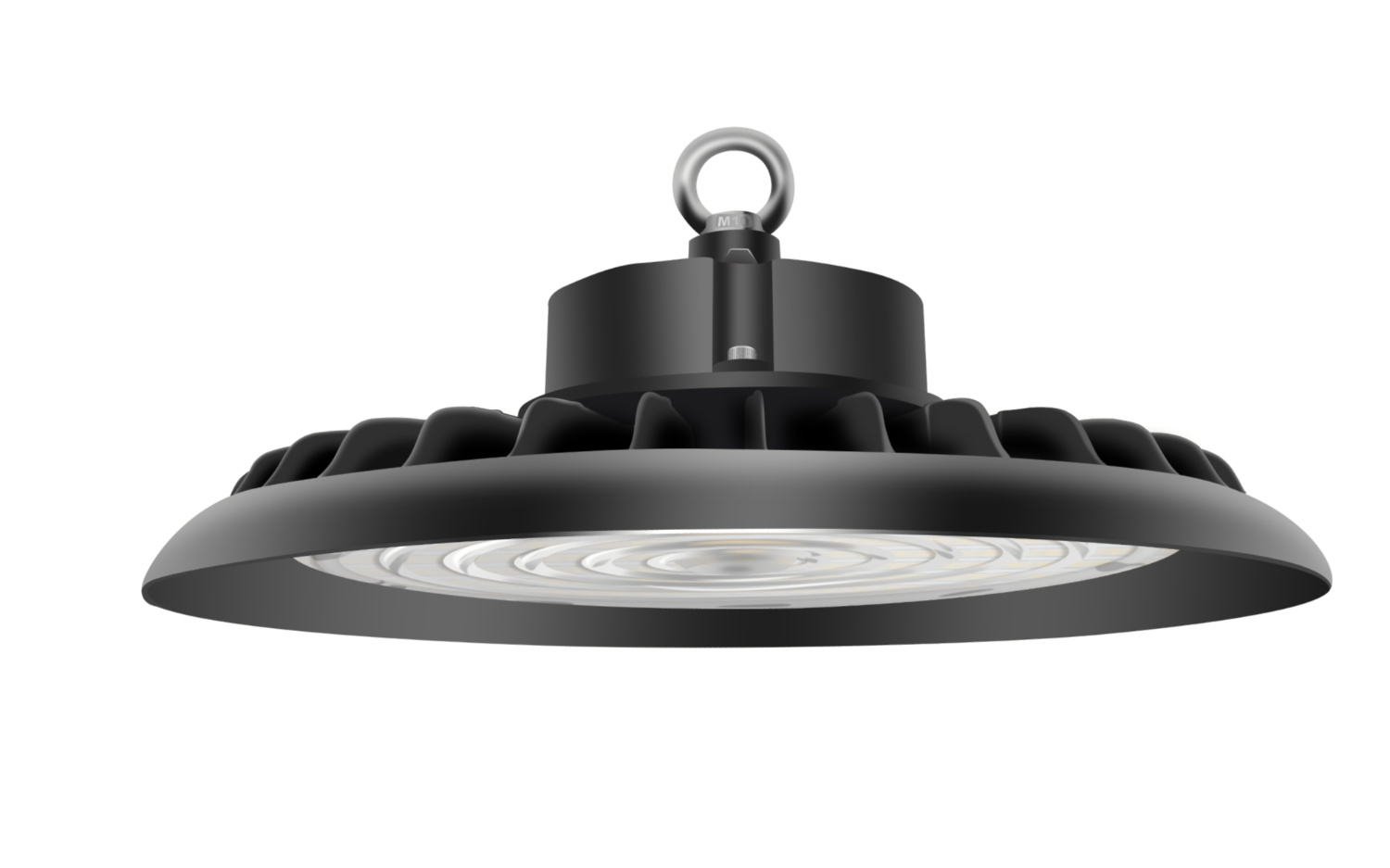

Sensors compatible with CAE products:
- PIR motion sensors (ceiling or fixture mount)
- Photocell modules for daylight tracking
- Zigbee/Bluetooth smart nodes for central control
If you’re using BMS platforms, most of these can plug in directly using standardized wiring protocols or mesh control nodes.
Challenges We’ve Run Into—and Solved
Not every data hall is sensor-friendly. Here are a few curveballs:
- Reflected IR: Glass surfaces sometimes throw off PIR sensors
- False triggers: Vibration from cooling fans triggering ultrasonic sensors
- Maintenance: Dust on sensors = misreads. Wipe them monthly.
Best solution: Dual-tech sensors with smart logic timers and a maintenance checklist tied to your facility schedule. We’ve baked this into several service contracts for clients in Penang and Selangor.
Are Photocells and Occupancy Sensors Worth It?
If your energy bill’s over five figures monthly, yes. Absolutely.
| Metric | Without Sensors | With Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Energy Cost | ~$6,000 | ~$4,200 |
| Average Payback | – | 12–18 months |
| HVAC Load Impact | Full lighting heat | 20–30% reduction |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Are photocells useful inside a sealed, windowless data hall?
A: No. Use them in corridors or entry zones with natural light exposure. Occupancy sensors are better inside halls.
Q: Do occupancy sensors work with all LED fixtures?
A: Only if drivers support 0–10V dimming or relay switching. CAE’s SeamLine Batten and Quattro lines are sensor-compatible.
Q: Can sensors interfere with Wi-Fi or radio signals?
A: Rarely, but cheap unshielded PIR models can cause localized EMI. Stick to vetted industrial-grade units.
Q: How often should I recalibrate sensors?
A: Every 6–12 months, or after any major rack/room layout change.
Q: Can I use both photocells and occupancy sensors together?
A: Yes. Photocells control based on light levels; occupancy handles presence. Use both for max savings.